Importance of Flexural Testing:
The primary purpose of flexural testing is to measure how materials perform under flexural stress conditions. This is critical because many engineering applications involve materials being exposed to bending forces rather than pure compression or tension. Flexural strength and modulus are key properties that can indicate how a material will react to bending and deformation, providing insight into its stiffness, strength, and resistance to permanent deformation.
Key Parameters Measured
The ASTM D790 Standard ASTM D790 outlines the method for testing the flexural properties of plastics and similar materials. Here is an overview of the procedure:
According to ASTM D790, the test specimens are prepared from molded, extruded, or fabricated sheets. Specimen sizes are critical, with the standard dimensions typically being 125 mm in length, and either 12.7 mm in width and 3.2 mm in thickness, or other dimensions as specified in the material’s classification.
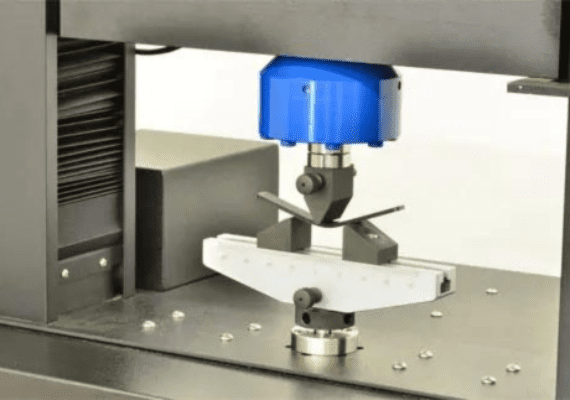
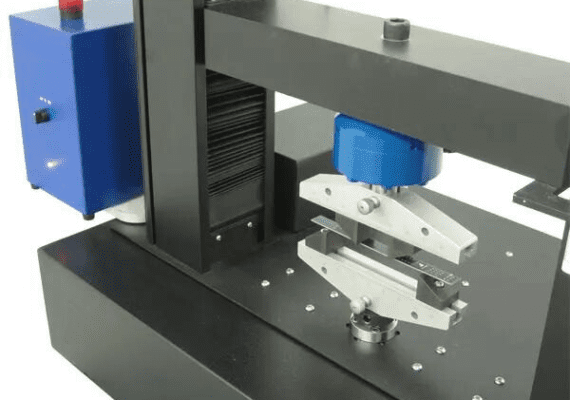
The test is conducted using a universal testing machine equipped with a flexural fixture. The specimen is positioned horizontally over two supports, and a load is applied at the center via a loading nose until the specimen fractures or the maximum strain level is achieved.
The typical test setup involves a three-point bending fixture, where the specimen is supported at two points and loaded at the midpoint. The span length between the supports is calculated based on the thickness of the specimen to ensure a valid test.
The data obtained from ASTM D790 flexural testing provides essential insights into the material’s behavior under bending stresses. These include:
ASTM D790 flexural testing is a crucial procedure for evaluating the bending behavior of plastics and other materials. By following the specific guidelines laid out in the standard, manufacturers and engineers can ensure that materials are suitable for their intended applications and meet the necessary performance criteria. Whether for material selection, research, or quality assurance, flexural testing provides valuable data that can directly impact product design and application success.